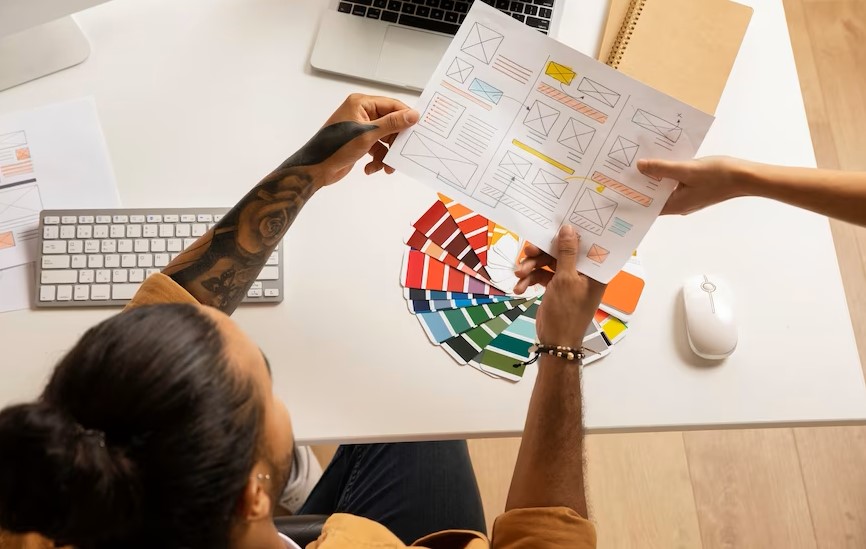
Saul Bass, a graphic designer, known for his design of film posters, has said, “Design is thinking made visual.”
You might have heard this story of the 2000 U.S Election, where faulty design played a big role in choosing the President of the United States. The Palm Beach county had a butterfly design which resulted in confusion. Over 1800 people voted for the Reform Party instead of the Democrats and this created a lot of confusion. In the end, the entire election was won by George Bush of the Republican Party, with less than 600 votes. How did this happen?.
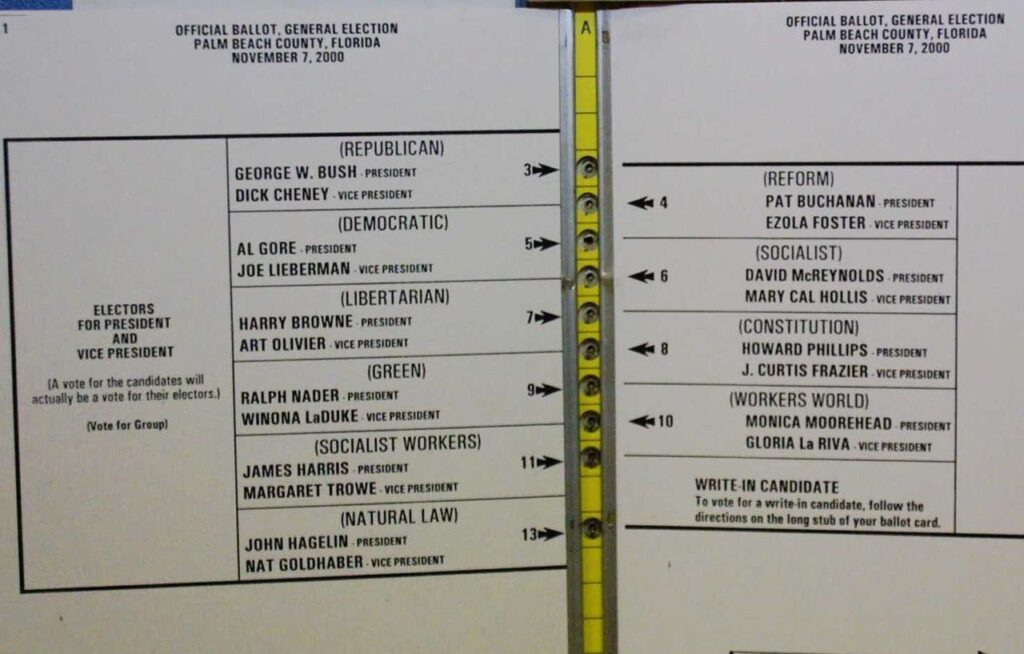
In this case, a faulty design which ignored the user perspective was responsible. Designers have a responsibility to present a neutral view of the solution to all the stakeholders.
Design Thinking helps designers look at a challenge to gain knowledge, develop insights and identify opportunities before designing solutions. A design centric culture must develop strategic intent.
Innovation has taken over human centered processes, services and products. Designers are now as much involved in creating ideas than solely dressing them up. One of the best examples of innovation in products was the how the telephone evolved. From being a tool for communication. The telephone has evolved. The rotary phone was the result of users wanting the phone to be convenient for them to use near the desks and table, rather than that being attached to the wall. The rotary slowly gave way to a dialpad then the next stage of design thinking evolved it into the modern ubiquitous smartphone that we see today. What needs to be noticed here is the importance of design thinking that has brought about a change in the way we work. The term itself has been coined recently, but elements of design thinking have been essential to our current objects.
Design studio such as Worxwide Consulting play an essential role in meticulously crafting design elements for both electoral campaigns and businesses, ensuring effective communication and mitigating potential misunderstandings.
Let’s explore more about design thinking and how we can make the most of it?
Design thinking is a systematic visual approach to tackling problems and generating new avenues of opportunities. For instance, if you want to build a disruptive new product or customer experience or are planning to take the business to the next level (Read, How to Develop a compelling value proposition) the Design Thinking approach touches everywhere. It’s design principles contribute significantly to elevating the success rate for innovation at each stage. This can be easily seen in all successful design-centric companies such as Apple, Google, Dyson, and Tesla.
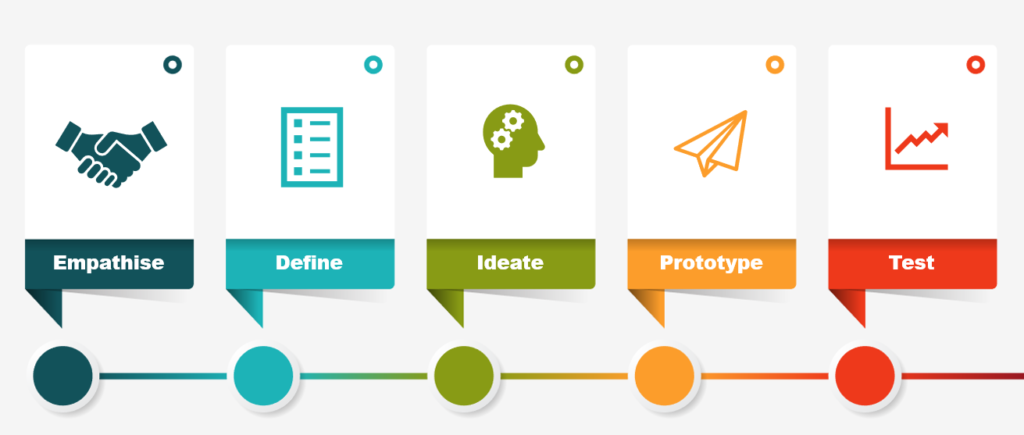
Empathize
Empathizing is central to the design thinking process. It is significant to listen to your customers’ needs, requirements and wants relative to the particular problem. For designers, it is important to understand the users and know how they feel while interacting with a product interface. An empathetic designer can create products that not only please the end-user but also make their lives easier.
Empathy is the starting point for any design project and is phase one of the Design Thinking process. During this phase, designers spend time getting to know the user and understanding their requirements. This phase also means observing and engaging with the end-user to understand their psychological and emotional level. It requires setting aside assumptions, suspending your view of the world around you, and seeing it from the end users’ perspective. A designer involved in Design Thinking starts by gathering real insights about the user.
Define
After the Empathy – 1st stage of Design Thinking Process, designers move ahead to analyse the information gathered and draw conclusions to make the gathered information insightful.
After the empathy stage where designers observe and understand the end-user by putting themselves in their shoes, the next stage is to interpret the observations to understand the underlying problem.
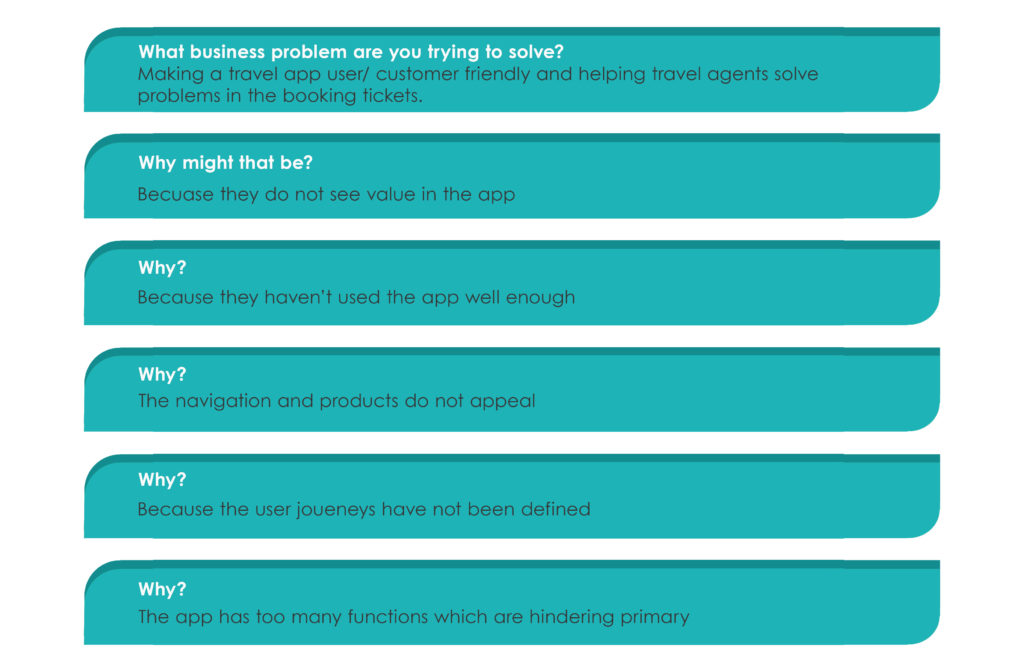
Let is consider a case where a travel company has not been able to get their agents to use their platform. The travel agents prefer other modes rather than using the problem. We try to dig deep and try finding the answers, which are hidden and do require a level of deep probing.

That means, in this stage, designers try to define the problem statement. An aspect that design thinking proves vital is at articulating and framing a problem clearly to devise solutions and explore opportunities. The more efficient problems are pinpointed and framed. Subsequently, more avenues and solutions open up for tackling the laid down problems.
Ideate
The third component of the design thinking process is ideate; it is the most interesting yet most rigorous. In this phase, design thinkers are supposed to bring as many ideas as possible to the problem statement identified in the define stage. The only task of design thinkers is to think of as many solutions as possible, brainstorming for ideas without thinking much about their feasibility or viability.
Once the problem is framed, designers think of creative ways to tackle the problem. They must spur as many ideas as possible. Design thinkers put enough stress that we must not ignore ideas that seem obvious or easy during this phase. Any idea can lead to a brilliant concept. So, they must make sure to look into each and every idea with a fresh mindset. To finalize this stage, shortlist the best and leave the rest.
Thinkers also resort to putting their thoughts on boards, sticky notes, sketching, chart papers, mind maps, etc. They also try taking inspiration and build on the ideas of other design thinkers. Later as part of the process, all the suggested ideas by design thinkers are brought to the table at one place, thought over, revisited.
Mind maps are often used during the research phase while trying to understand a subject. In the Design Thinking process, mind maps are crucial to the first three stages, i.e., empathizing, defining, and ideating.
Prototype
Before releasing a product to market, product designers along with the entrepreneurs, want to test the product if it is working fine. It must solve the user’s problem exactly as it intended?
Prototyping comes fourth in the design thinking process. Building prototypes will be based on everything that the design thinkers have achieved so far. Prototypes of the products will reflect insights gathered from users via interviews, defining problem statements, ideating solutions.
But what is a prototype?
Through prototyping, the solution is brought into vision. Different methods are put in use, such as sketching, rapid prototyping and many others. The main intent of this stage is to create rough drafts of solutions to decide if these will prove beneficial for the problem.
A simple, economical approach is followed while prototyping; according to the context, the prototype can be transformed into a beta product or a minimum viable product (MVP). Using agile project management or the lean startup methodology to manage MVP and its development can be useful.
Test
Next is testing. In this stage, design thinkers take their product out to test with end-users to monitor their response and deem whether the solution satisfied them or not.
Implement
And finally, we commercialize the product or service. The design thinking cycle follows the same circle when further features and enhancements are added to a product or service offering.
Design Thinking has passed way beyond a design philosophy into an agile methodology that tests products along way the process of creation. It is a process of how design thinkers explore and solve problems.
How BidsandBeyond can help you?
Our UI/UX certified experts practice Design Thinking Agile approach with right mix of content, creativity and user experiences. Bids and Beyond will handhold you from ideation to design to market; including business and technical brainstorming. We have a dedicated team of digital innovators, growth consultants and UI UX designers to help you build long-term relationships beyond revenues with your clientele.
Worxwide Consulting, a top management consulting firms that help companies drive digital growth by improving user and customer experience. We help companies with end-to-end product design or UX design services that include research, strategy, design, test product designs, and prototypes. Worxwide is based out of the US, UK, and India offering bid consulting, sales transformation, user experience, and customer experience design services.
tx, USA

London, UK

India


